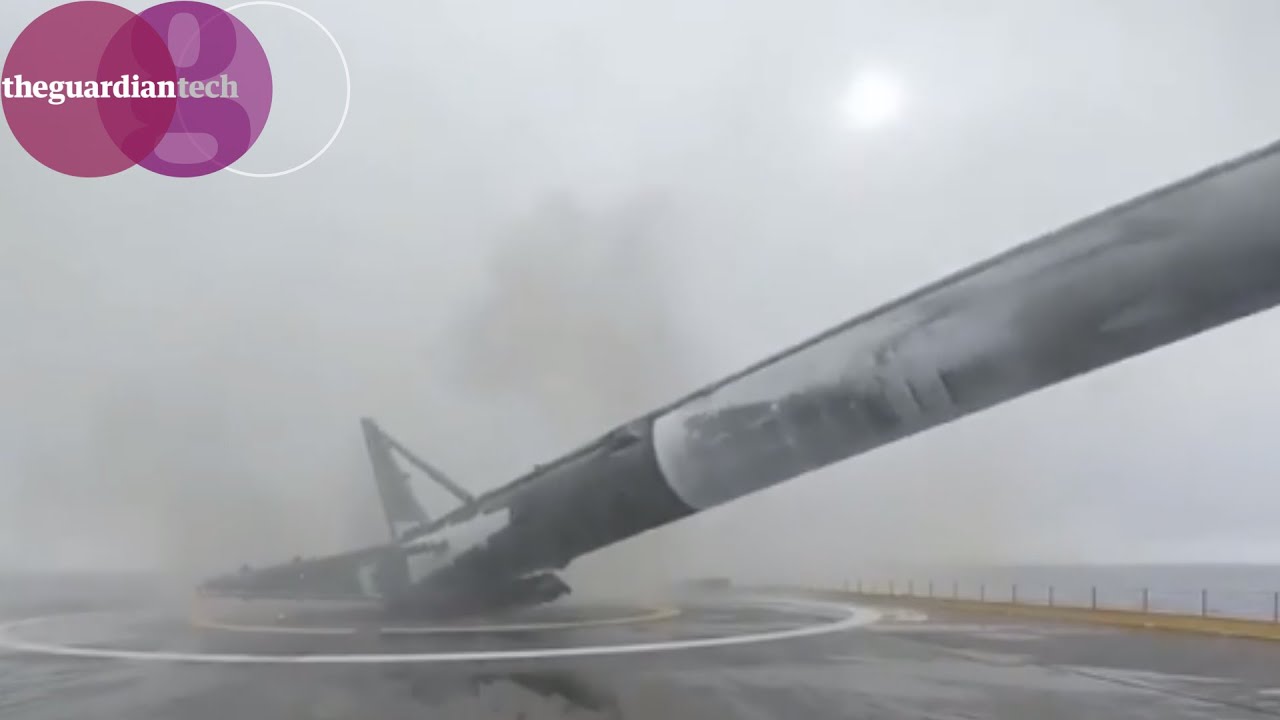
The recent SpaceX explosion during the inaugural launch of the Starship rocket has sent shockwaves through the aerospace sector. This unexpected turn of events raises questions about the future of private space exploration. As everyone tries to catch their breath, industry experts are deep-diving into the implications of this failure. So, grab your favorite snack and let’s explore the potential consequences and the lessons learned from the SpaceX explosion, as well as how competitors and regulators are responding.

1. The Immediate Impact of the SpaceX Explosion
The SpaceX explosion caught many off guard, especially with the company’s impressive record of successful launches. Here’s how the response unfolded:

2. Comparing SpaceX’s Response to Past Failures
Failures are part and parcel of the aerospace world. Reflecting on SpaceX’s situation, let’s look at how it stacks up against other notable incidents:
3. Industry Reactions to the SpaceX Explosion
What’s the industry buzzing about now? Responses from competitors paint a colorful picture in the aftermath of the SpaceX explosion. Here’s a peek:

4. Lessons Learned from the SpaceX Explosion
Failures often bestow valuable lessons, and the SpaceX explosion is no exception. Let’s break down the key takeaways:

A New Era in Space Exploration
The SpaceX explosion is a stark reminder that the journey into outer space is not without its risks. This mishap doesn’t only impact SpaceX; it casts a wider net over the entire aerospace sector. The evolving strategies, shifts in investor confidence, and possible regulatory changes may well define how commercial space exploration unfolds in the coming years.
As the industry reflects on this incident, one thing is clear: the commitment to safety and innovation will be at the heart of future explorations. The narrative of space travel is still bright, even if it’s a bit bumpy right now. Here’s to hoping the next chapter brings more triumphs than those setbacks caused by the SpaceX explosion!
SpaceX Explosion Stuns Industry: Fun Trivia and Interesting Facts
The Incident That Took the Industry by Storm
On April 20, 2023, the SpaceX explosion during its highly-anticipated Starship launch sent shockwaves through the aerospace industry. For those unfamiliar, this was the first test flight of the SpaceX Starship, which aims to revolutionize space travel. The launch was built up as a milestone event, comparable to iconic moments in aviation history. Unfortunately, things took a turn when the spacecraft exploded just a few minutes after liftoff, leaving fans and industry experts alike reeling. It’s almost like the unpredictability of the comedy scene at a Baltimore comedy club; everyone waits for that punchline that might never land.
Debunking Myths: The Reality Behind Space Exploration
Space travel is no joke. While the SpaceX explosion would seem like a monumental failure, it actually shines a light on the rigorous processes behind aerospace development. Did you know that most rocket tests don’t go as planned? In fact, many past successful missions experienced their own share of hiccups before taking to the stars! It’s a bit like figuring out How do people become dead inside ? The answer reveals a lengthy journey filled with trials and errors. It’s crucial for companies like SpaceX to learn from every setback—consider it akin to fashion trends, where experimenting with spring Dresses For Women can yield surprising results.
What’s Next for SpaceX?
Despite the setback with the SpaceX explosion, the company is ardently pursuing its goals for Mars colonization and beyond. In fact, interested spectators are already anticipating the next launch. Rumor has it, there might be even more captivating tech improvements. Speaking of captivating tech, the development of the Starship is much like the delightful cast of My Dress up Darling Characters, who each have specific roles in their creative adventure. Each Starship test ultimately helps build towards a future where interplanetary travel could become a reality, keeping excitement in the air like the buzz from weed And Adderall in young adult culture.
So, while this explosion was dramatic, it’s important to remember that failures pave the way for innovations and successes—and that’s the name of the game in this ever-expanding universe of possibilities!

Why did SpaceX explode today?
The explosion today was due to multiple engine failures in the spacecraft, which occurred during its launch from SpaceX’s private Starbase site. This led to a catastrophic failure before the booster and the spacecraft could separate.
How many SpaceX rockets have blown up?
SpaceX has seen a handful of rocket failures, with two in-flight failures and another partial success. The most notable ones are the CRS-7 mission and the recent explosion of the Starship during its inaugural flight, along with a failure during the Falcon 9’s landing attempt.
What went wrong with the SpaceX Starship?
The Starship’s inaugural launch went sideways when several of its 33 engines failed. This malfunction prevented the booster from separating from the spacecraft, ultimately leading to an explosion just four minutes after liftoff.
What rocket exploded in 2024?
In 2024, the notable rocket explosion involved a SpaceX Starship during its first launch attempt, which resulted in a major failure and crash into the Gulf of Mexico.
Is SpaceX going to Mars in 2024?
As of now, there aren’t any confirmed plans for SpaceX to go to Mars in 2024. The company continues its work on Starship but is facing challenges with successful launches.
What happens if there is a hole in the ionosphere?
A hole in the ionosphere can interfere with radio signals and satellite communications, as it disrupts the transmission of electromagnetic waves.
Did the SpaceX explosion cause a hole in the atmosphere?
The recent SpaceX explosion didn’t cause any holes in the atmosphere. Such occurrences are rare and typically wouldn’t be linked directly to rocket malfunctions.
Who owns SpaceX?
SpaceX is owned by Elon Musk, who founded the company to advance space technology and exploration.
What was the cause of the Starship failure?
The cause of the Starship failure was linked to several of its methane engines failing, which prevented a successful separation of the booster from the spacecraft before the explosion.
What is the top speed of SpaceX?
SpaceX rockets can achieve speeds up to 17,500 miles per hour during their missions, particularly when entering orbit.
Why has SpaceX stopped launching Starship?
SpaceX has temporarily halted Starship launches to analyze the recent failures and ensure that all technologies are functioning properly before continuing.
How will Starship be caught?
SpaceX plans to catch Starship using a system of robotic arms, designed to grab the vehicle as it descends, helping to minimize recovery efforts.
What will happen in 2024 in space?
In space, 2024 is expected to be significant, with planned missions and advancements in technology that could pave the way for future exploration efforts.
What famous spaceship exploded?
One of the most famous spaceship explosions is the Space Shuttle Challenger disaster in 1986, which also brought attention to the risks involved in space travel.
What is the goal of Starship?
The goal of Starship is to enable human exploration of Mars, facilitate long-term colonization, and make space travel more affordable and reusable.
What caused Starship 2 to explode?
The recent Starship explosion was caused by engine failures during the launch, preventing it from achieving its planned mission objectives.
Did SpaceX have an accident?
Yes, SpaceX has had accidents, including the recent Starship explosion and previous issues with Falcon 9 missions, but the company continues to learn and improve from these experiences.
What was the Starship launch for?
The Starship launch was intended for a series of test flights designed to evaluate the vehicle’s capabilities and gather data for future missions to destinations like Mars.
What is the purpose of the Starship Rocket?
The purpose of the Starship rocket is to transport humans and cargo to various destinations in space, including the Moon and Mars, ultimately aiming for interplanetary travel.